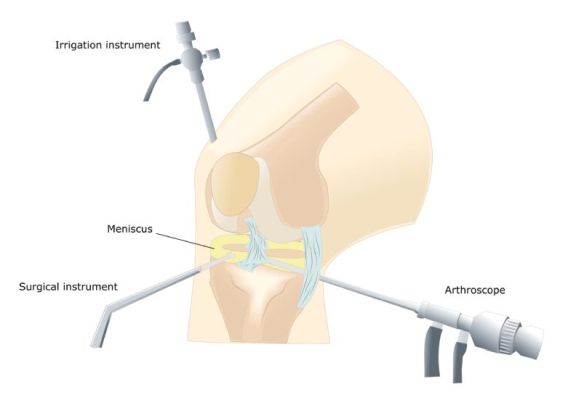
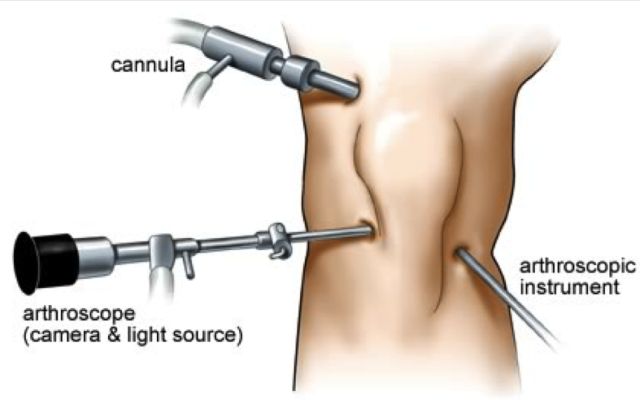
Pain in the hip joint is most often the result of osteoarthritis and can seriously affect your ability to lead a full and active lifestyle. Hip osteoarthritis is called coxarthrosis in medicine.
Endoprosthesis of the hip joint can help relieve pain and return to normal life. Over the past 20 years, thanks to the introduction of new materials and techniques into practice, the results of endoprosthetics operations have significantly improved.
Endoprosthesis of the hip joint is becoming more and more prevalent as the world's population is aging. At the moment,
hip replacement surgery in Delhi is the most commonly performed in the world.
HIP ANATOMY
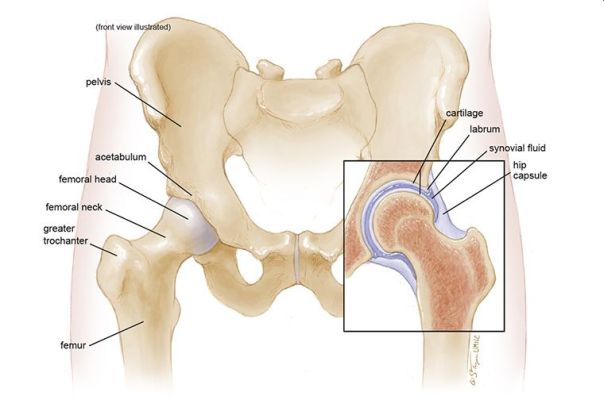
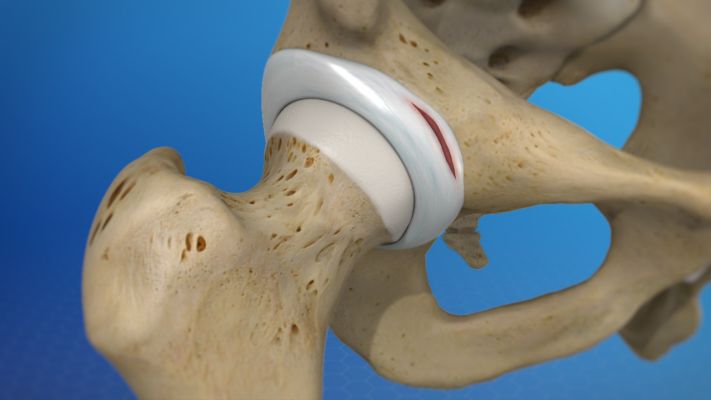
The hip joint is spherical in structure, so movements in it are possible in many planes. The joint is formed by the acetabulum, forming, as it were, a deep bowl and the head of the femur, which has the shape of a ball, explains the
orthopaedic in Delhi.
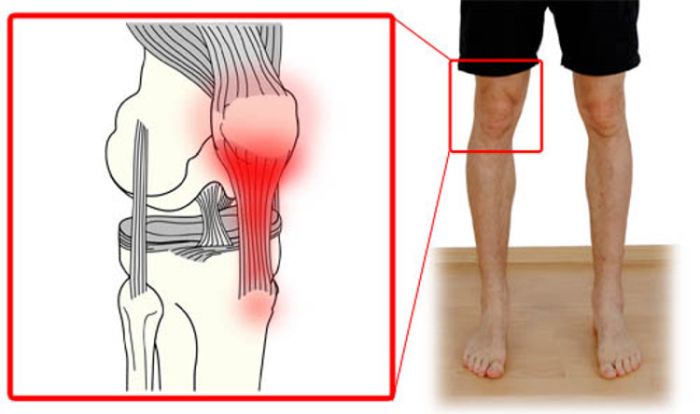
The femoral head is connected to its main part (diaphysis) using a short portion of the bone called the femoral neck. Strong and thick muscles and tendons surround the joint. The surfaces of the acetabulum and femoral head are covered with articular cartilage. The thickness of the articular cartilage is about half a centimeter in large joints. The articular cartilage is a hard and smooth material covering the bones in the joint area. The articular cartilage allows the bones coated with it to glide smoothly relative to each other without being damaged. The color of the articular cartilage is white and shiny.
The joint is surrounded by a dense waterproof capsule, inside which a special fluid is produced that lubricates the mating surfaces. The bones in the joint hold tight ligaments and muscles together. The design of the hip joint provides extremely high mobility while maintaining satisfactory stability. The powerful muscles around the joint allow us to move for a long time in an upright position, and also, if necessary, accelerate when running and jumping. Important nerves and blood vessels also pass around the joint.
WHEN CAN ENDOPROSTHETICS REQUIRED?
The main indications for
hip replacement in Delhi are arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis), fracture of the femoral neck, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.
With arthrosis, degenerative changes in the articular cartilage occur, which ultimately leads to cartilage wear. Bone growths (osteophytes) form around the joint.
Due to the deterioration of the cartilage, a decrease in its thickness, a significant decrease in smoothness, as well as a change in the shape of the articular surfaces, the friction in the joint increases, which leads to pain and a progressive violation of the movements in the joint.
Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is another cause of destruction of the hip joint. With this disease, the femoral head loses blood supply and actually collapses. The shape of the femoral head changes, the bone tissue making up the head is resorbed.
The articular surfaces of the acetabulum and the femoral head cease to correspond in shape, pain and impaired movement in the joint appear. The causes of the disease can be previous hip dislocations, birth injuries, prolonged treatment with corticosteroids, as well as some infections.
The main goal of replacing the joint in any of the degenerative diseases with an artificial one is to reduce pain and return movements. To do this, damaged surfaces are replaced with artificial ones, as a result of which the smoothness and painlessness of movements in the joint returns.
In case of fractures of the femoral neck, the blood supply to the head is disturbed, in connection with which its gradual destruction occurs.
Fracture fusion in these conditions is impossible,
hip replacement surgery in Delhi is the only way to activate the patient and return him to everyday activity.
PREPARATION FOR HIP JOINT REPLACEMENT
The decision about the operation is made by the
orthopaedic doctor in Delhi together with the patient. After clarifying the medical history, the doctor performs a thorough clinical examination to measure the current range of motion, the level of pain, the patient’s functionality. During the examination of the patient, the
orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi examines the radiographs, as well as the data of CT and MRI studies.
A thorough and complete medical examination before surgery is also required. This is done in order to minimize the risk of complications during
hip replacement surgery in Delhi. If a long-term operation or hemoglobin level of the patient is expected to be below normal values, a blood transfusion may be required after or during the operation. Mandatory prophylaxis of thromboembolic complications.
TYPES OF ENDOPROSTHESES
There are several main types of endoprostheses - cementless and cement.
Cemented endoprostheses are held in the bone using a special cement that fixes the metal to the bone. The surface of cementless prostheses is made in such a way that the bone tissue grows into it over time, due to which the prosthesis is held in the bone. In order for the endoprosthesis to grow, the bone is treated with special tools.
Both types of fixation of endoprostheses are widely used in medical practice. Also, in some cases, a combination may be used where, for example, the acetabular component (cup) is fixed with cement, and the femoral component (leg) is cementless. The decision about whether to use a cement or cementless endoprosthesis is made by the
orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi based on the age, lifestyle of the patient and the quality of his bones.
The endoprosthesis consists of two main parts.
The acetabular component (cup) replaces the articular surface of the acetabulum. The shell of the acetabular component is made of metal, inside of which is placed a plastic or ceramic insert that is directly in contact with the femoral component.
The femoral component replaces the head and neck of the femur, usually made entirely of metal. In some designs of the endoprosthesis, the head may be made of ceramic.
Endoprosthetics can be total when both components are replaced, and unipolar. With unipolar endoprosthetics (hemiarthroplasty), only the femoral component changes. Hemiarthroplasty is usually performed for fractures of the femoral neck in elderly and debilitated patients.
With this type of endoprosthetics, the earliest verticalization of the patient is allowed, the very next day. This significantly reduces the risk of thromboembolic and hypostatic complications in elderly debilitated patients with femoral neck fractures. Equally important is the shorter operation time for hemiarthroplasty compared with total arthroplasty, which also reduces the risks during anesthesia and blood loss during surgery. Currently, our clinic uses modern cemented bipolar hip arthroplasty. A bipolar endoprosthesis is a modern type of unipolar prosthesis in which the head is double.
A similar design of the endoprosthesis increases the life of the prosthesis, increases its stability and range of motion.
MORE ABOUT HIP JOINT OPERATION
The
orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi performs access to the hip joint, a skin incision is performed in the upper third of the thigh. After the hip joint is exposed, surgeons dislocate the worn femoral head from the acetabulum.
Then, a resection of the damaged head and neck of the femur is performed with a special electric saw.
Then, using special mills, the acetabulum is processed. During the treatment, the worn cartilage is completely removed and a hemisphere is formed into which the acetabular component will be implanted.
After the formation of the acetabulum, the surgeon fills the cavity with bone cement and establishes a suitable acetabular component. At this stage, the correct spatial orientation of the acetabular component at the right angle is important. This affects the life of the endoprosthesis and the likelihood of complications in the postoperative period.
After cement hardens and fixation of the acetabular component, the surgeon proceeds to the femur. At this stage, the bone canal of the femoral canal is developed with special rasps to the required size.
Next, cement is placed in the prepared canal in the femur and the femoral component is installed.
A head of the required size is selected and the femoral component is set into the acetabular.
As soon as the surgeon is convinced that everything is set properly, the wound is sutured in layers. Drainages are established for a day. The patient is sent to a special ward in the postoperative ward, explains the
orthopaedic in Delhi.
From the first day, rehabilitation of the patient begins.