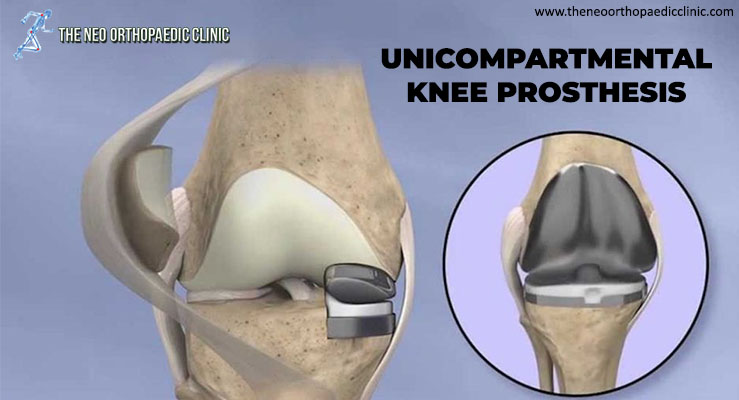
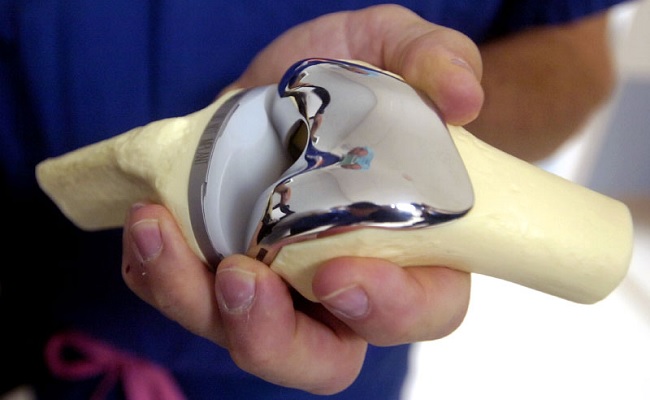
During knee replacement surgery in Delhi, the damaged bone and cartilage are covered with metal and plastic components. In a unicompartmental knee replacement (also called a “partial” knee replacement), only part of the knee is covered. This procedure is an alternative to total knee replacement for patients whose disease is limited to just one area of the knee.
Because partial knee replacement is done through a smaller incision, patients generally spend less time in the hospital and return to normal activities sooner than patients undergoing total knee replacement.
ADVANTAGES OF PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
Several studies show that most patients who are suitable candidates for the procedure have good results with unicompartmental knee replacement in Delhi.
The advantages of partial knee replacement over total knee replacement include:
- Faster recovery;
- Less pain after surgery;
- Less blood loss;
DISADVANTAGES OF PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
The disadvantages of partial knee replacement compared to total knee replacement include:
- Slightly less predictable pain relief;
- Potential need for more surgery. For example, a total knee replacement in Delhi may be necessary in the future if arthritis develops in the parts of the knee that were not replaced;
SURGERY CANDIDATES
If your osteoarthritis has advanced and non-surgical treatment options are no longer relieving your symptoms, orthopaedic in Dwarka may recommend knee replacement surgery in West Delhi. In order to be a candidate for unicompartmental knee replacement, your arthritis must be limited to one compartment of your knee. In addition, if you have any of the following characteristics, you may not be eligible for the procedure:
- Inflammatory arthritis;
- Significant knee stiffness;
- ligament damage;
With proper patient selection, modern unicompartmental knee replacements have demonstrated excellent mid- and long-term results in younger and older patients.
YOUR SURGERY
A partial knee replacement operation typically lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
Partial knee replacement. There are three basic steps in the procedure:
- Prepare the bone. Your orthopaedic surgeon in Dwarka will use special saws to remove cartilage from the damaged compartment of your knee;
- Position the metal implants. The removed cartilage and bone are replaced with metallic coatings that recreate the joint’s surface. These metal pieces are typically held in the bone with cement;
- Insert a spacer. A plastic insert is placed between the two metal components to create a smooth gliding surface;
COMPLICATIONS
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks involved with a partial knee replacement. Your orthopaedic surgeon in West Delhi will discuss each of the risks with you and take specific steps to help prevent potential complications.
Although rare, the most common risks include:
- Blood clots. Blood clots in the leg veins are a common complication of knee replacement surgery. Blood clots can form in the deep veins of the legs or pelvis after surgery. Blood anticoagulants such as low molecular weight heparin and aspirin can help prevent this problem. Newer medications, such as rivaroxaban (Xarelto), may also be prescribed by your orthopaedic doctor in Dwarka, depending on your needs;
- Infection. After surgery, an infection may occur in the skin over the wound or deep into the wound. An infection can happen while you are in the hospital or after you go home. You will be given antibiotics before the start of your surgery and these will be continued for about 24 hours afterwards to prevent infection;
- Nerve or vessel damage. Although it rarely happens, nerves or blood vessels can be injured or stretched during the procedure;
- continued pain;
- Risks of anesthesia;
- Need for additional surgery;
RECOVERY
Hospital discharge. Patients with partial knee replacement generally experience less postoperative pain, less swelling, and have easier rehabilitation than patients undergoing total knee replacement. In most cases, patients go home 1 to 3 days after the operation. Some patients go home on the day of surgery.
Weight support. You will begin putting weight on your knee immediately after surgery. You may need a walker, or crutches for the first few days or weeks until you feel comfortable enough to walk without assistance.
Rehabilitation exercise. A physiotherapist in Dwarka will give you exercises to help maintain your range of motion and restore your strength.