What is Achilles tendon rupture?
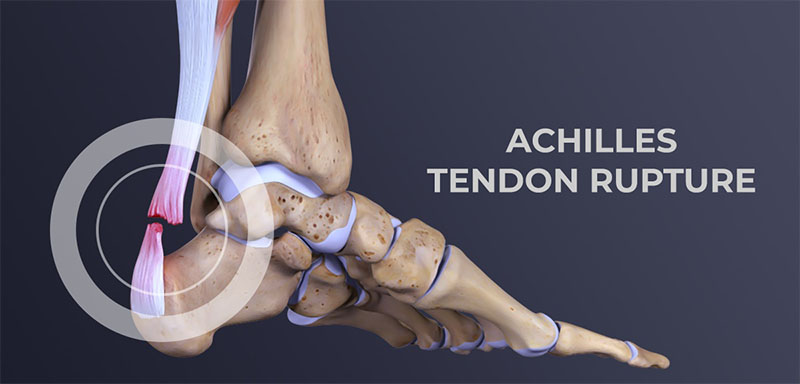
An Achilles tendon rupture or rupture occurs when the tendon “ruptures or tears” leading to separation or discontinuity in the tissues that make up the tendon.
In terms of anatomy, the Achilles tendon, a sort of fibrous “ribbon” or “cord” that connects muscle to bone, is the largest and strongest tendon in the body that connects the calcaneus (heel bone) to the medial gastrocnemius muscles., lateral gastrocnemius and soleus muscles (popularly known as calf muscles or “leg belly” muscles). When the muscle contracts, it “pulls” the tendon, which in turn moves the foot.
The rupture often reflects the previous existence of tendinosis phenomena caused by sports microtraumas or degeneration (aging) of the tendon. In most cases, the tear occurs at the bottom of the tendon (just above the heel), but it can occur anywhere along the tendon. In the presence of a healthy tendon, the lesion can appear in the bone or muscle.
Total ruptures, partial ruptures
We can generically classify Achilles tendon ruptures into:
- Total rupture – in the total rupture of the Achilles tendon, the tissues break completely, that is, the tendon is completely “separated”.
- Partial rupture – in a partial rupture of the Achilles tendon, the tendon does not completely rupture, only an incomplete rupture occurs. Partial tears can vary greatly in severity according to the extent of the injury.
A total rupture is more frequent than a partial rupture. As a rule, a total rupture is a more serious injury when compared to a partial rupture and with more exacerbated symptoms. A partial tear can also present with pain that can range from moderate to severe and, if not recognized, it can quickly progress to a total tear.
See more information on treatments to better understand the different therapeutic approaches according to the extent of the lesion.
Achilles tendon rupture – causes
The Achilles tendon can lose elasticity and become “weak and thin” with age and lack of use. Then, it becomes prone to injury or breakage.
Rupture is more common in people with pre-existing Achilles tendonitis (tendon inflammation). Repetitive tendinitis and the consequent calcifications are a risk factor for tendon rupture.
Certain diseases (such as arthritis and diabetes) and medications (such as corticosteroids, for example) can also increase the risk of rupture.
Rupture occurs most often in the middle-aged male athlete. The injury usually occurs during recreational sports that require impacts with the ground, running, jumping, etc. Most of the time, these are football, athletics, tennis, basketball, among others. Injury can happen in these situations as a result of traumatic dorsiflexion when the muscle is strongly contracted causing it to tear.
Breaks can, however, also occur in everyday activities. For example, when falling from a significant height, when entering a pothole abruptly, traffic accidents, etc.
Achilles tendon rupture – symptoms
The signs and symptoms of Achilles tendon rupture are:
- Sudden, severe pain may be felt in the “back” of the ankle or the “tummy of the leg”, often described as “being hit by a rock or shot” or “like someone stepping on the back of the ankle”;
- A loud clicking sound can be heard;
- A discontinuity (“gap”) or depression (void) can be felt and seen in the tendon above the calcaneus (heel bone);
- Inability to stand on tiptoe on the affected side;
- Initial pain, swelling (swelling) and stiffness may be followed by bruising and weakness (not being able to land on the foot, walking).
Achilles tendon rupture – diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by the orthopaedic doctor in Delhi after collecting the clinical history, performing the physical examination and some complementary means of diagnosis (MCDT).Bottom of Form
A simple test is to “stretch” the “calf or calf muscles” while lying on your stomach (Thompson test). In the impossibility of being able to elevate the foot, there is, most likely, a rupture in the tendon. This test isolates the connection between the “calf muscles” and the tendon and eliminates other tendons that may still allow poor movement.
The orthopaedic doctor in Dwarka may order the following tests to confirm the diagnosis and to know in greater detail the location and degree of severity of the lesion:
- Plain radiography (XR) – not being a very useful exam, it can identify a bone fragment avulsion of the calcaneus;
- Ultrasound or ultrasound – Ultrasound of the leg and thigh can help assess the possibility of deep vein thrombosis and can also be used to rule out a Baker’s cyst (or cyst). Ultrasound can identify Achilles tendon rupture or signs of inflammation (tendinitis or tendinosis);
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – MRI is extremely sensitive for diagnosis and allows you to determine if there is still a tendon in continuity. It allows other diagnoses such as tendinitis, tendinosis and bursitis.
Pain in the “back of the heel” is not always due to an Achilles tendon rupture. In the differential diagnosis, tendinitis (inflammation of the Achilles) and bursitis (inflammation of the bursae) should be considered, among the most frequent pathologies that cause pain in the Achilles region.
Achilles tendon rupture – treatment
The objective of the treatment is to restore the function of the tendon, for this, it is necessary that the tissues that make up the tendon heal “united” with each other. In this way, it will be possible for the patient to return to the same level of activity before the injury. Regaining Achilles tendon function after an injury is critical to making walking possible.
Treatment reflects a balance between tendon protection and initial movement. Protection is necessary to allow time for healing and to prevent further injury. Moving the foot and ankle is necessary to prevent stiffness and loss of muscle strength.
We can divide treatment options into surgical and non-surgical. Conservative (non-surgical) treatment consists of a set of therapeutic attitudes aimed at healing the tendon and restoring its function without resorting to any type of surgical intervention.
The choice between surgical and non-surgical treatment can be controversial in some cases. Both surgical and non-surgical treatment will require an initial period of approximately six weeks of immobilization. For most patients, both treatment options have good functional results.
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT
Nonsurgical treatment is often used for non-athletes or for people with a low general level of physical activity who will not benefit from surgery. In the elderly and people with clinical complications, conservative (non-surgical) treatment should also be considered as a first option.
Initially, a cast below the knee is performed with the foot in equinus (foot in marked plantar flexion, “down”). Although it is not routine, it is possible to perform an MRI to verify that the tops of the tendon are in contact. The cast is changed, at intervals of two to four weeks, to slowly stretch the tendon back to its normal length. This treatment usually takes 8 to 12 weeks. During this period, global strengthening and flexibility exercises are taught.
SURGERY (SURGICAL TREATMENT)
Surgery on Achilles tendon rupture is often indicated in healthy and active people who want to resume activities such as walking, running, cycling, etc. Even those who are less active may be candidates for surgical repair of the tendon. The decision to operate should be discussed with your orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi.
Surgery should not be performed if there is an active infection or damaged skin at or around the Achilles tendon rupture site. In addition, some diseases or lifestyle habits, such as diabetes, smoking habits, sedentary lifestyle, steroid use and inability to follow instructions after the operation, may be a contraindication for surgery.
Surgical intervention for an Achilles tendon rupture is usually performed on an outpatient basis. This means that the patient is operated on and goes home the same day.
We can identify two distinct surgical approaches:
The first is to perform the intervention percutaneously, allowing to perform a minimally invasive surgery, through small incisions. A kind of needles with attached sutures are passed, allowing the Achilles tendon to be sutured.
The second approach is the open approach (traditional method, where the surgeon makes an open incision to access the tendon). This starts with an incision made in the back of the leg, just above the calcaneus (heel bone). After the best orthopaedic in Dwarka finds the two ends of the torn tendon, these ends are sutured. The incision is subsequently closed.
The surgical technique will be previously determined by the orthopaedic in West Delhi, depending on the type and location of the rupture, among other factors. In the postoperative period, regardless of the surgical technique chosen, the patient is immobilized with an equinus foot.
Despite being a safe surgery, some complications can arise, such as risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels and bleeding or blood clots, among others. A new rupture can also occur (recurrence).
Recovery after surgery
After the surgery, the patient is placed with a splint or a “plaster boot” from the foot to the knee. Usually, the patient cannot walk or put weight on the involved leg. Crutches, a walker or a wheelchair are used to allow the patient to remain mobile for the first few times. Patients are encouraged to keep the operated leg elevated above the level of the heart to decrease swelling (swelling) and pain.
Patients are usually seen in the office two weeks after surgery. The splint or cast is removed, and the surgical incision is evaluated. Stitches are usually removed at this point if necessary. After two to six weeks, depending on postoperative protocol and orthopedic in Dwarka preference, patients may be allowed to begin performing some force. For this, a “hiking boot” can be used. Ankle movement is often allowed and encouraged.
After six weeks, full-body strength is generally allowed. Physiotherapy in Dwarka will need to be started and is intended to restore ankle range of motion. Strengthening of the “calf muscles” and Achilles is gradually allowed as the tendon heals. It is usually possible to resume full activity after six months. Recovery time after surgery can extend up to a year, until the patient can achieve full rehabilitation.
Even in cases where surgery is performed, the above-mentioned therapeutic attitudes are included in the rehabilitation plan. See more information on conservative treatment.