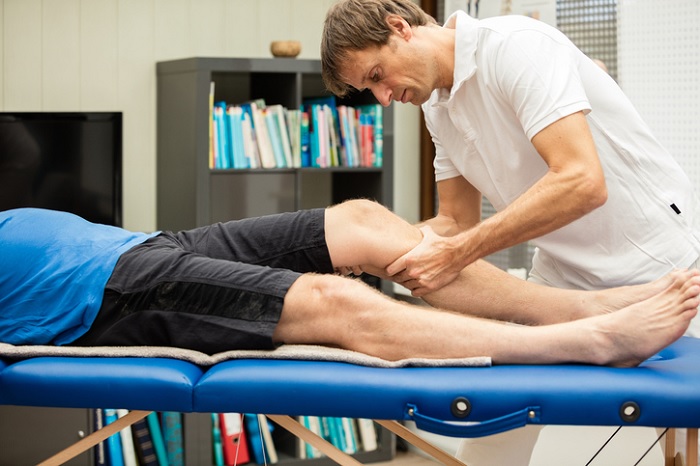
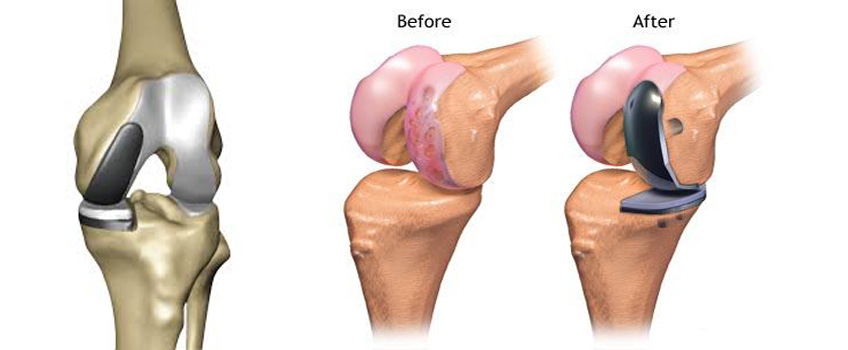
Recovery from arthroscopy knee surgery is much faster than traditional surgery. However, it varies depending on which area has been operated and the method used by the orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi. This involves torn meniscus, cruciate ligaments, synovial membrane, patella misalignment, broken joint cartilage and other pathologies such as Baker's cyst.
Tips to follow
As a rule, the recovery time of a knee arthroscopy in Dwarka depends on how long it takes for the inflammation caused by surgery to disappear. The patient should follow some tips such as:
- Use crutches for eight or ten days.
- Put your knee high using several cushions to cushion, in order to control swelling the days after surgery.
- Not standing for a long period of time, or doing any exercise until your doctor tells you to.
- Take pain relievers to alleviate pain.
- Take anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen, and get cold in the area.
- Start exercising to boost your area's musculature, when your physiotherapist in Dwarka advises you.
In most cases, the time off for a knee arthroscopy in Dwarka is estimated at one month. From that moment on, the patient can regain his or her normal routine.
The same is not true if the patient has undergone a more complex surgery such as meniscal repair. Here the immediate postoperative is heavier, although the results are very good. After the surgery, the advice of orthopaedic in Delhi should be followed and the knee should not bend more than 60 degrees or carry weight on the operated leg the first month. During that time you have to use crutches, avoiding supporting your foot and having your knee suffer. After 30 days you have to start a progressive rehabilitative treatment, from least to most. Recovery lasts about 3 or 4 months. After this time the patient regains mobility in the joint and can reach its previous sporting level, explains the best knee surgeon in Delhi.
After surgery, some precautions should be taken to prevent wounds from becoming infected. The incisions should be kept clean and dry while the stitches are maintained. It is recommended to cover the operated leg with a plastic, when the patient is going to shower, to protect it from moisture and water. Routine checks are common for the specialist to assess development. Your orthopaedic in Tilak Nagar will also indicate when you can drive again, although it usually will take one to three weeks.
Rehabilitation and exercises
Rehabilitation following a knee arthroscopy in Dwarka seeks full joint recovery, returning tone, strength and mobility. In athletes, this step, prior to full recovery, is very important to get back to their sporting level before the injury. The type of injury marks when rehabilitation needs to begin and how it should be done, says the sports injury specialist in west Delhi.
There are exercises the patient can do at home. The most common ones, which can be done sitting or standing are:
- Contract the quadriceps, pressing the knee and holding for five seconds.
- Raise your legs about 30 cm and keep them stretched with your foot in a flex position (planting dorsiflexion) for a few seconds.
Both require about 10 repetitions. Also, when crutches are no longer used, the orthopaedic in Delhi recommends:
- Carry weight on the knee gradually.
- Perform joint bending and extension exercises.
- Up and down stairs
- Walk
After a knee arthroscopy in Delhi, most people in a month resume their normal activity and work, although in some cases they may need to use crutches. In certain surgerys, recovery lasts for several months.