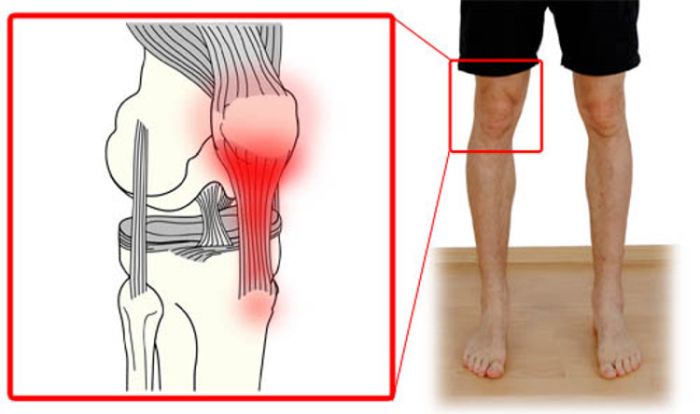
Tendinitis is an inflammatory condition that develops in the patellar tendon, due to twists, tears, or tendon damage. Tendons are fibers that connect muscles to bones. Knee tendinitis occurs most often due to overuse of the knee joint.
Patellar tendinitis is known as knee tendinitis. Patellar tendon is an injury that occurs in the tendon that connects the patella to the leg, called a patellar tendon. The patellar tendon works with the muscles at the front of the thigh to extend the knee so you can run, kick and jump.
Knee tendinitis is a common condition in athletes whose sports involve running and jumping. But it is not a unique condition of athletes, people who do not perform deportation can suffer from knee tendinitis.
Knee tendinitis can be a serious condition that needs attention and treatment, as they can eventually worsen tendon damage and require surgery for treatment, says the orthopaedic in Delhi.
Knee Anatomy
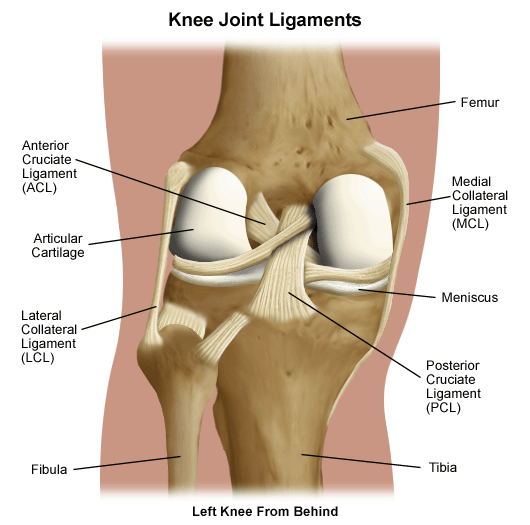
The knee is composed of 3 bones. The thigh bone that is the femur, the largest leg bone that is the tibia and patella that slides into a groove at the end of the femur.
Tendons are strong tissues that connect muscles to the bone. Its size and shape vary, there are small tendons in the fingers and large in the legs. The patellar tendon plays an important role in maintaining the label in place and in straightening the knee.
Symptoms of knee tendinitis
Pain is the first symptom of knee tendinitis. Pain can manifest directly on the patellar tendon and manifest in cases such as;
- At first, pain may be present at the start of physical activity or after intense exercise.
- The pain gets worse that interferes with your activities, whether it's sports or everyday activities like climbing stairs or getting up from a chair.
- Pain when bending the knee
In addition, pain may be stiff in the knee, especially when jumping, crouching, sitting, kneeling.
Should I see a specialist?
Sometimes knee pain can improve with self-care measures and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs, but you may need to visit orthopaedic clinic in Delhi if:
- Pain continues or gets worse
- Interferes with the realization of your daily activities
- You have swelling or redness around your knee
Why does knee tendinitis occur?
Knee tendinitis or patellar tendinitis is a common overuse injury caused by constant, repetitive stress on the patellar tendon. Stress causes small tears in the tendon, which as they multiply cause pain and inflammation, explains the sports injury specialist in west Delhi.
Risk factors
Factors that may contribute to the development of knee tendinitis include:
- Physical activity or sports. Running and jumping are the movements most associated with tendinitis
- Tight leg muscles. Tightening the quadriceps and hamstrings can increase tension in the patellar tendon.
- Muscle imbalance. If some muscles are stronger than others, the stronger ones can pull the tendon harder and marry an imbalance. This uneven pull can cause knee tendinitis.
Complications
If no care is received and despite the pain continues to perform activities, it can attract ever larger tears in the patellar tendon. Pain and reduced knee function can persist, if the problem is not addressed, and more serious patellar tendencies can progress, warns the orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi.
Get ready for your appointment
If the pain persists during or after certain activities and does not improve with self-care measures. Your orthopaedic doctor in Delhi may refer you to a sports medicine specialist.
Before you go to your appointment with your orthopaedic in Delhi, you can prepare with:
- List of their symptoms, how they manifest and when they started.
- Medical information such as medications and supplements if you take them.
- Duration and intensity of your sports practice
- Resentful injuries
- Questions you want to ask your doctor
Diagnosis
Knee tendinitis can be diagnosed by reviewing your clinical history, physical knee exam, and performing imaging tests.
During the physical exam, your doctor may apply pressure to your knee to determine where you feel pain and may ask you to perform certain movements against resistance. Knee tendinitis pain is usually felt in the front of the knee under the patella.
Image testing
Some tests that may be suggested to you include:
- Radiography. They can be used to exclude bone problems that can also cause knee pain.
- Ultrasound. They may reveal tears in the patellary tendon.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Create detailed images that can show changes in the patellar tendon.
Knee tendinitis treatment
It is usually started with non-surgical treatment. There are several treatment options that can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Small tears can be treated with non-surgical treatment. A splint, or brace may be required to provide rest to the tendon and to heal the tendon. But treatment will depend on different factors such as age, level of physical activity, size and type of tendon tear.
Therapy
Physical therapy can help restore function, decrease pain and prevent future injuries.
- Stretching exercises. These types of exercises can reduce muscle spasm and help lengthen the muscle-tendon unit.
- Strengthening exercises. Weak muscles contribute to the tension of the patellar tendon.
- Patellar tendon strap. Apply pressure to the tendon to help distribute strength away from the tendon.
Other treatments
If nonsurgical treatments don't help, your orthopaedic in Delhi may suggest other therapies such as:
- Corticosteroid injections. Corticostoirdes are ultrasound-guided around the patellar tendon and help relieve pain. They are, however, this treatment can have consequences, such as weakening tendons and making them more prone to ruptures.
- Surgery. Surgery may be necessary for repair of tendons that rupture as a result of chronic degeneration and inflammation. Most people with tendon tears may require surgery to reattach the patella tendon. The surgical technique used varies depending on the condition. Some procedures may be performed through minimally invasive surgery, through small incisions around the knee, explains the best knee surgeon in Delhi.
Prevention
To reduce your risk of developing or worsening knee tendinitis, you may:
- Don't play with the pain. As soon as you feel pain, apply self-care methods such as applying ice and rest until your pain is silky, and avoid activities that cause stress on your tendon.
- Strengthen muscles. Strong muscles are better able to handle the tendon that can cause knee tendinitis.
- Improve technique. Make sure you are doing your activities in the right way, consider taking classes to better learn your technique when you are starting a new sport.
Recovery
Full recovery can take half a year to a year, depending on the extent of the injury and the treatment required.


No comments:
Post a Comment