Overview
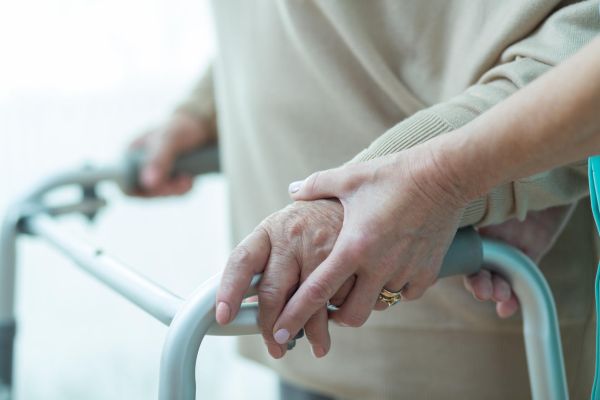
A hip fracture means more than a broken bone. For the elderly, hip fracture means a major change in life.
Most likely, surgery will be needed, and recovery may take more than a year, says orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi. The activity and physical therapy, but also the help of the family and a caregiver will contribute to the recovery of mobility.
Most hip fractures are suffered by people over the age of 65. Those in this age group must be very careful to avoid falls.
In most people, the hip fractures in the upper thigh (femur), close to where the thigh bone joins the hip joint.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a hip fracture include:
- Inability of the person to move immediately after a fall
- Severe pain in the hip or groin area
- Inability of the person to maintain weight on the leg from the body in which the fracture occurred
- Stiffness, bruising and local swelling
- Shortening of the foot on the side where the hip was injured
- External orientation of the foot on the side where the fracture occurred.
Causes
Falls are the leading cause of hip fracture in older adults. As people age, their bones become less resilient and are naturally prone to breakage, even after minor trauma. Children and young adults are more likely to have hip injuries, says the orthopaedic in Delhi.
The causes of hip fractures include:
- Female gender
- The presence of weak and tall people in the family or common cases of fractures among family members, in old age
- Unhealthy eating habits, inadequate calcium, and vitamin d intake
- Lack of activity
- Smoking
- Medical conditions that cause dizziness and balance problems or conditions such as arthritis which can interfere with the balance of the body
- The use of certain drugs that can lead to bone loss
Risk factors
Among the risk factors that can increase the risk of rupture of the hip bones are:
- The number of hip fractures increases substantially with age. As a person gets older, bone density decreases, vision and balance become weaker, and reaction time slows down. The combination of these factors can increase the risk of hip fracture.
- About 80% of hip fracture cases are reported in women. Women lose bone density faster than men because the decrease in estrogen levels that occurs with menopause accelerates bone loss.
- Chronic medical conditions. osteoporosisis the most important and best-known risk factor for hip fractures, but other medical conditions can increase the risk of bone weakening. Other conditions include endocrine disorders, such as hyperthyroidism and intestinal disorders characterized by low absorption of vitamin D and calcium.
- Certain medications. Some medications, usually those used for chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and asthma, have a gradual effect on bone health when used long-term.
- Nutrition problems. Lack of calcium and vitamin D in youth reduces bone mass and increases the risk of fractures later in life.
- Lack of physical activity. Some types of weight training and walking also help strengthen bones and muscles, and the risk of fractures will be lower.
- Tobacco and alcohol consumption. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with normal bone growth and remodeling processes, resulting in bone loss.
Complications
A hip fracture is a serious injury. Although the fracture itself is treatable, complications can endanger a person's life. If a person suffers from a hip fracture, surgery may be necessary.
The orthopaedic in west Delhi may use an external traction system that will allow the hip to heal. The biggest risk when using this system is that it can cause muscle damage and weakness, increasing the likelihood of permanent loss of mobility.
In addition, traction will keep the patient immobilized for a long time, during which time blood clots can develop in the veins of the legs.
Affected veins can be located on the surface of the skin, causing thrombophlebitis superficial or may be located deeper, in the muscles, resulting in deep vein thrombosis.
The risks of using the traction system include:
- The appearance of blood clots
- Bedsores
- urinary tract infections
- pneumonia
- Muscle weakness.
Treatment
Your orthopaedic doctor in Delhi will advise your patient to exercise as soon as possible after surgery. This helps prevent complications such as pneumonia, blood clots and scabies.
After the operation, it will be difficult for the patient to do many of the activities alone, so it may be necessary to be admitted to a rehabilitation center for a period after the operation. The more active a person is, the faster he will recover.
Ways to prevent
There are many steps that can be taken to prevent a hip fracture. One of the most important is to prevent osteoporosis, which can occur in both women and men. To slow down and prevent osteoporosis the orthopaedic in Dwarka advices to follow:
- Eat foods rich in calcium, milk, cheese, yogurt, dark green vegetables, seafood, almonds, but also supplements with calcium and vitamin D
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Some people will need treatment to slow the progression of osteoporosis
- Prevention of falls is very important
- Furniture, carpets, and electrical cables in the house will be arranged in such a way as to avoid bumps and other accidents
- Will not walk on ice
- Wear shoes with a sturdy, flat sole
- Have regular eye exams
- Exercise to maintain strength and balance
- Constantly take the medications recommended by the orthopaedic in Delhi, noting that some medications such as birth control pills sleeping, or painkillers may increase the risk of falls.