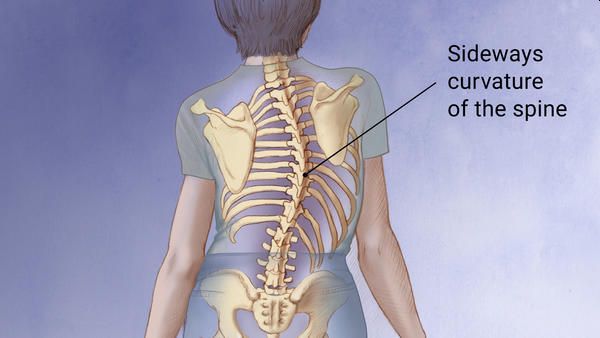
Scoliosis produces a more or less pronounced curvature in the spine and can be treated in various ways. Gait studies have an important role in its diagnosis and prevention.
When we talk about scoliosis, we immediately understand that we are referring to a curvature of the spine, but it should be noted that not all column curvatures are, says the orthopaedic in Delhi.
Curves derived from postural "bad habits", reflex curvatures caused by pain or contractures, or compensatory "scoliosis", in which the curvature occurs to compensate for other asymmetries, are not considered scoliosis.
Causes and symptoms of scoliosis
Depending on the type of scoliosis, these will have one or the other causes. As a general rule, scoliosis due to malformations is congenital, but can also manifest itself from other diseases. Despite this, most scoliosis is idiopathic, appears in childhood or adolescence, and its causes are unknown, explains the orthopaedic in Delhi.
Scoliosis, although congenital, is not detected in the new-born, but appears progressively in childhood and stabilizes when bone growth ends, after puberty, even increasing in old age if degenerative phenomena appear.
It should be noted that neither the postures adopted by the child, nor the intense practice of exercise increases the risk and that the greater the degree of curvature there is a greater volume of scoliosis in girls than in boys.
Studies show that scoliosis does not produce more back pain or more intense pain than patients who do not have it, at least in slight curvatures, nor that 'straightening' the spine leads to significant improvements in the quality of life of those who suffer it, except the merely aesthetic.
In severe curvatures it can present chronic back pain or in extreme cases even affect breathing or some organs, says the orthopaedic doctor in Delhi.
Scoliosis Treatment
Considering that scoliosis does not produce pain or relevant limitations - by itself and in degrees of slight curvature - the chosen treatment and its impact should be considered based on its consequences, that is, not choosing an overly aggressive treatment for a problem (scoliosis) whose effect is mainly aesthetic.
Depending on the degree of scoliosis, the indicated treatments (in order) are:
- Non-specific exercise: It simply seeks to improve the muscular and cardiovascular state, it has positive effects in terms of prevention and evolution of back pain, which is why it is highly recommended for children both for scoliosis itself and for their general health. and to establish in the child that healthy habit.
- Specific exercise: Traditionally it was prescribed with the idea of developing muscles with the ability to reduce scoliotic curvature, but there is no evidence of its effectiveness in this regard, although it does exist when it comes to reducing the prescription of the brace.
- Corset: Its only objective is to stop the development of the curvature, but its continued use can generate muscular atrophy. Although the materials of current corsets are much more flexible to be more comfortable, they are less effective than rigid ones. Even so, the observable changes in a patient with a brace and another without a brace are not very relevant, so its use is being rethought - especially in children.
- Surgery: Only cases of scoliosis associated with other diseases or malformations need to be operated, so it would not make sense to submit a patient with idiopathic scoliosis to a surgical process since the risks and scars are considerable to obtain a merely 'aesthetic benefit. '. The surgery is aggressive and usually has relevant complications in 10.2% of the operated, some examples are; wound infections, respiratory or implant complications. In addition, scoliosis surgery involves loss of mobility of the spine or limitation of rotational movements, depending on the area of the spine affected, explains the orthopaedic surgeon in Delhi.
Prevention
Although due to the origin of this 'disease' it is difficult to prevent it in most cases, there are certain recommendations to prevent it or not make it worse. The practice of exercises to strengthen the area, the practice of swimming (an exercise whose benefits for the back in general are well known), the correct postural hygiene, not abusing heels and visiting regularly a physiotherapist to assess our state and help us not aggravate scoliosis are the most common forms of 'prevention'.
Gait studies also play an important role in the diagnosis and prevention of scoliosis, especially in children and adolescents in whom it is still possible to act because they are in the growth phase, says the orthopaedic in Delhi.